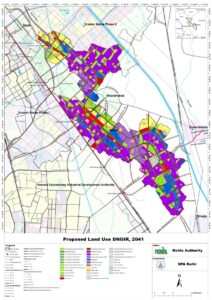
Greater Noida Master Plan 2041: Overview
The Greater Noida Master Plan 2041 is a comprehensive framework developed to guide the planned growth and development of Greater Noida. It focuses on integrating residential, commercial, industrial, and infrastructural needs while ensuring sustainability and addressing environmental concerns. The planning area includes Phase 1 and Phase 2 of Greater Noida, covering both urban and rural settlements with a total area of approximately 713.27 sq. km.

Key Elements of the Master Plan
1. Residential Development (Yellow Zone)
- The plan allocates a significant portion of the land for residential purposes to accommodate the projected population growth by 2041. As per the master plan, Phase 1 has achieved much of its proposed residential development, with housing zones expanding primarily in the north, central, and southern areas.
- The population projections for 2041 estimate Greater Noida’s population to reach 40 lakhs (4 million), requiring careful planning of housing infrastructure.
2. Commercial Development (Red Zone)
- Commercial zones are spread across Greater Noida with an emphasis on creating hubs near transportation corridors for accessibility. The plan supports Mixed Use – Hospitality and Commercial Centres to foster economic activities in these areas.
- Commercial belts are strategically placed near industrial sectors and along arterial roads like the 130 m wide Noida-Greater Noida Expressway, ensuring that these zones are easily accessible and well-integrated with residential areas.
3. Industrial Areas (Purple Zone)
- Industrial sectors are a crucial part of Greater Noida’s economic engine. The plan envisions substantial industrial growth, particularly in Phase 2, with sectors designed for electronics, automobiles, pharmaceuticals, and more.
- Key industries like Honda, Yamaha, Oppo, and several others have set up operations in these zones, driving employment and economic growth.
4. Transportation Infrastructure (Various Lines)
- The transportation infrastructure is one of the plan’s strongest pillars. The Noida-Greater Noida Expressway, Eastern Peripheral Expressway, and Yamuna Expressway form the backbone of the city’s road network, ensuring connectivity to Delhi, Ghaziabad, and other parts of Uttar Pradesh.
- Plans for enhanced rail connectivity include Western and Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridors and a proposed Multi-Modal Transport Hub (MMTH) at Boraki, which will act as a logistics hub for freight and passenger movement.
- Metro expansion is also included, with routes connecting Greater Noida to Jewar International Airport and central Noida to boost public transport options.
5. Green and Recreational Areas (Green Zones)
- Environmental sustainability is a key focus of the plan. The 5000 hectares designated for green areas will include parks, recreational spaces, and ecological zones such as the Hindon riverfront and the surrounding green buffer zones.
- A City Forest and Waterfront Development along the Hindon River are integral parts of the green infrastructure aimed at promoting biodiversity and improving the quality of life for residents.
6. Institutional and Public Utility Areas (Brown and Blue Zones)
- The master plan emphasizes the development of institutional areas including schools, hospitals, and public utilities to meet the needs of the growing population. Sectors such as Knowledge Parks have been earmarked for higher education and research institutions.
- Public utilities, such as power, water supply, and waste management, are strategically planned to support the future population. The plan includes provisions for solar power plants and sewerage treatment facilities to ensure environmental sustainability.
7. Special Zones
- Special Economic Zones (SEZ) and Logistics Parks are critical parts of the industrial strategy, promoting investment and economic growth. These areas will serve as hubs for industries like IT, biotechnology, and high-tech manufacturing, catering to both domestic and international markets.
Projections and Future Growth
The population projection for 2041 is a major driver of the land-use planning, with a targeted population of 40 lakhs. The development strategy includes:
- Transit-Oriented Development (TOD) to maximize the use of land around transport hubs.
- Mixed-use developments to optimize space utilization in both commercial and residential areas.
- Expansive infrastructure upgrades, including road networks, Rapid Rail Transport System (RRTS), and metro connections to facilitate easy commuting and reduce congestion.
Environmental and Ecological Considerations
The plan emphasizes the protection and integration of natural resources, including:
- Water bodies and wetlands to preserve biodiversity.
- Reserved forests and green buffers to mitigate the environmental impact of urbanization.
- Attention to flood-prone areas and a focus on disaster management, particularly in relation to air pollution and seismic activity.
Conclusion
The Greater Noida Master Plan 2041 is a comprehensive guide aimed at balanced growth, economic prosperity, and environmental sustainability. The plan leverages Greater Noida’s strategic location near Delhi, ensuring it continues to attract investments while maintaining a high standard of living for its residents. With its focus on industrial growth, residential expansion, and infrastructure development, Greater Noida is poised to become a major hub in the National Capital Region.